Đừng bỏ lỡ những tính năng hấp dẫn của Baitap365.com
Grammar builder and reference
Tiếng Anh 12 Grammar Builder and Reference - Unit 6
Tiếng Anh 12 Grammar Builder and Reference - Unit 7 Tiếng Anh 12 Grammar Builder and Reference - Unit 8 Tiếng Anh 12 Grammar Builder and Reference - Unit 5 Tiếng Anh 12 Grammar Builder and Reference - Unit 4 Tiếng Anh 12 Grammar Builder and Reference - Unit 3 Tiếng Anh 12 Grammar Builder and Reference - Unit 2 Tiếng Anh 12 Grammar Builder and Reference - Unit 1 Tiếng Anh 12 Grammar Builder and Reference – IntroductionTiếng Anh 12 Grammar Builder and Reference - Unit 6
1 Complete the sentences with the verb in brackets i n the correct passive form.2 Rewrite the sentences in the passive. Remember that the indirect object usually becomes the subject. 1 Complete the second sentence in each pair so that it means the same as the first.
6.1 The passive - Bài 1
6.1 The passive
(Bị động)
• We form the passive with the verb be and the past participle of the main verb. The object of an active verb can become the subject of a passive verb.
They haven’t found a cure for colds yet.
→ A cure for colds hasn’t been found yet.
• We use the passive when we do not know or do not want to say who or what is responsible for the action.
This photograph was taken in India.
• If we mention the agent, we use by.
Enormous public baths were built by the Romans.
• With verbs that often have two objects (ask, award, give, offer, owe, pay, send, show, teach, tell, etc.), either object can become the subject of a passive sentence.
They gave me my money back.
→ I was given my money back.
→ My money was given back to me.
It is much more common for the indirect object (usually a person) to be the subject of the passive sentence (example a above).
• We use the past continuous and present continuous forms of the passive, but not other continuous forms as they sound unnatural.
A celebration is being planned.
→A celebration has been being planned.O
→ They have been planning a celebration.P
Tạm dịch
• Chúng ta tạo thành thể bị động với động từ be và phân từ quá khứ của động từ chính. Tân ngữ của động từ chủ động có thể trở thành chủ ngữ của động từ bị động.
Họ vẫn chưa tìm ra cách chữa cảm lạnh.
→ Cách chữa cảm lạnh vẫn chưa được tìm ra.
• Chúng ta dùng thể bị động khi không biết hoặc không muốn nói ai hoặc cái gì chịu trách nhiệm về hành động.
Bức ảnh này được chụp ở Ấn Độ.
• Nếu đề cập đến tác nhân thì chúng ta dùng by.
Những nhà tắm công cộng khổng lồ được xây dựng bởi người La Mã.
• Với những động từ thường có hai tân ngữ (xin, trao, cho, đề nghị, nợ, trả tiền, gửi, chỉ, dạy, kể, v.v.), cả hai tân ngữ đều có thể trở thành chủ ngữ của câu bị động.
Họ đã trả lại tiền cho tôi.
→ Tôi đã được trả lại tiền.
→ Tiền của tôi đã được trả lại cho tôi.
Thông thường tân ngữ gián tiếp (thường là người) là chủ ngữ của câu bị động (ví dụ a ở trên) là phổ biến hơn nhiều.
• Chúng ta sử dụng dạng quá khứ tiếp diễn và hiện tại tiếp diễn của thể bị động, nhưng không sử dụng các dạng tiếp diễn khác vì chúng nghe có vẻ không tự nhiên.
Một lễ kỷ niệm đang được lên kế hoạch.
→ Một lễ kỷ niệm đã đang được lên kế hoạch. O
→ Họ đang lên kế hoạch tổ chức một lễ kỷ niệm. P
1 Complete the sentences with the verb in brackets in the correct passive form.
(Hoàn thành câu với động từ trong ngoặc ở dạng bị động đúng)
1 The band’s new song _______________ (not / release) until next month.
2 A cure for cancer _______________ (not / discover) yet.
3 Those trees _________________ (plant) by my grandfather last year.
4 Hans _________________(show) around the college this morning.
5 When the onions are cooked, they _________________(add) to the sauce.
6 Technology _________________(improve) all the time.
7 The Colosseum _________________(build) by the Romans over ten years.
8 We _________________(tell) their decision in a few days’ time.
6.1 The passive - Bài 2
2 Rewrite the sentences in the passive. Remember that the indirect object usually becomes the subject.
(Viêt lại câu ở dạng bị động. Hãy nhớ rằng tân ngữ gián tiếp thường trở thành chủ ngữ.)
1 My brother lent me the money for the ticket.
2 They’ll allow us ten minutes to answer the questions.
3 A nurse has given the patient some medicine.
4 Your uncle is taking your parents to the airport now.
5 They didn’t give us any information about the strike.
6 A local man showed them the way to the river.
7 No one will forgive him if he keeps on lying.
6.2 The passive: advanced structures - Bài 1
6.2 The passive: advanced structures
(Bị động: cấu trúc nâng cao)
Verbs like believe, consider, expect, know, report, say and think are often used in passive constructions, especially in formal language.
• We can use an impersonal construction with it + passive: it + passive (present or past) + that…
It was believed by many people until the 19th century that tomatoes were poisonous.
It is now known that they are not.
• Alternatively we use a passive construction with an infinitive:
subject + passive (present or past) + to do / to have done.
Tomatoes were believed to be poisonous.
• We can use an impersonal construction with there + passive (present or past) + to do / to have done.
There are estimated to be 100,000 people at this weekend’s festival.
If the sentence refers to a present belief about a past event, we use the present simple passive followed by a perfect infinitive (to have done).
The thief is believed to have escaped to Scotland.
• We can use passive structures with present and past forms of modal verbs.
Phones should be switched off during the play.
• Verbs that are followed by an infinitive or gerund can also be followed by a passive infinitive or gerund.
Everyone likes to be praised.
I love being given surprise presents!
Tạm dịch
Các động từ như tin, cân nhắc, mong đợi, biết, báo cáo, nói và nghĩ thường được sử dụng trong các cấu trúc bị động, đặc biệt là trong ngôn ngữ trang trọng.
• Chúng ta có thể sử dụng cấu trúc khách quan với it + bị động: it + bị động (hiện tại hoặc quá khứ) + that…
Cho đến thế kỷ 19, nhiều người vẫn tin rằng cà chua có độc.
Bây giờ người ta biết rằng họ không phải vậy.
• Ngoài ra, chúng ta có thể sử dụng cấu trúc bị động với động từ nguyên thể:
chủ ngữ + bị động (hiện tại hoặc quá khứ) + to Vo / to have V3/ed.
Cà chua được cho là có độc.
• Chúng ta có thể sử dụng cấu trúc khách quan với There + bị động (hiện tại hoặc quá khứ) + to Vo / to have V3/ed.
Ước tính có khoảng 100.000 người tham dự lễ hội cuối tuần này.
Nếu câu đề cập đến niềm tin hiện tại về một sự kiện trong quá khứ, chúng ta sử dụng bbij động hiện tại đơn theo sau là một động từ nguyên thể hoàn thành (to have V3/ed).
Tên trộm được cho là đã trốn sang Scotland.
• Chúng ta có thể sử dụng cấu trúc bị động với các dạng động từ khiếm khuyết ở hiện tại và quá khứ.
Điện thoại nên được tắt trong khi chơi.
• Những động từ được theo sau bởi một động từ nguyên mẫu hoặc V-ing cũng có thể được theo sau bởi một động từ nguyên mẫu hoặc V-ing thể bị động.
Mọi người đều thích được khen ngợi.
Tôi thích được tặng những món quà bất ngờ!
1 Complete the second sentence in each pair so that it means the same as the first.
(Hoàn thành câu thứ hai trong mỗi cặp sao cho có nghĩa giống câu đầu tiên.)
1 They think that the thief escaped in a stolen car.
The thief _________________________________________.
2 It is known that too much fried food is bad for you.
Too much fried food _________________________________________.
3 The painting was thought to be an orginal Picasso.
It _________________________________________.
4 It’s reported that the earthquake caused extensive damage.
The earthquake _________________________________________.
5 They say that heavy rain has caused the floods.
Heavy rain _________________________________________.
6 They didn’t believe that his injuries were serious.
His injuries _________________________________________.
7 Some fruits are said by scientists to be ‘superfood’.
It _________________________________________.
6.2 The passive: advanced structures - Bài 2
2 Complete the sentences with the verbs below in the correct form.
(Hoàn thành các câu với các động từ dưới đây ở dạng đúng.)
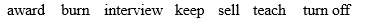
1 Use plenty of suncream to avoid ____________ by the sun.
2 Everyone expects her ____________ an Oscar for her latest performance.
3 No one wants ____________ waiting in a queue.
4 I can’t ____________ the right battery – this one doesn’t fit my tablet.
5 All mobile phones must ____________ during the film.
6 Do you remember ____________ how to ride a bike as a child?
7 They don’t think the singer will agree ____________.
Mẹo tìm đáp án nhanh
Search Google: "từ khóa + baitap365" Ví dụ: "Bài 5 trang 13 SGK Vật lí 12 baitap365